Appearance
原型对象prototype
原型是一个对象,我们称prototype为原型对象,原型的作用是共享方法。
比如说在构造函数中定义了一个函数,那么每次实例对象时都会在内存中给这个函数开辟一个空间,使用原型就可以共享函数避免这个问题。
javascript
function Star(name) {
this.name = name;
}
Star.prototype.sing = function () {
console.log('我会唱歌');
}
var vae = new Star('vae');
vae.sing()
__proto__
为什么可以通过Star.prototype.sing = function () {}使用构造函数prototype原型对象的属性,是因为每个实例对象都有一个对象原型__proto__指向构造函数的prototype原型对象
vae.__proto__ === Star.prototype他们完全相等__proto__不能直接当属性使用,他相当于一个线路,提供一个查找机制,指向构造的prototype
原型的constructor
prototype中又有一个constructor属性指向了他所在的构造函数,通过这点我们可以在给原型对象赋值时直接赋值对象,再通过constructor指回原来的构造函数。(不指回原来的构造回丢失原来prototype内的属性)
javascript
Star.prototype = {
constructor : Star,
sing: function(){
console.log('我会唱歌');
},
movie: function(){
console.log('我会演电影');
}
}
原型链
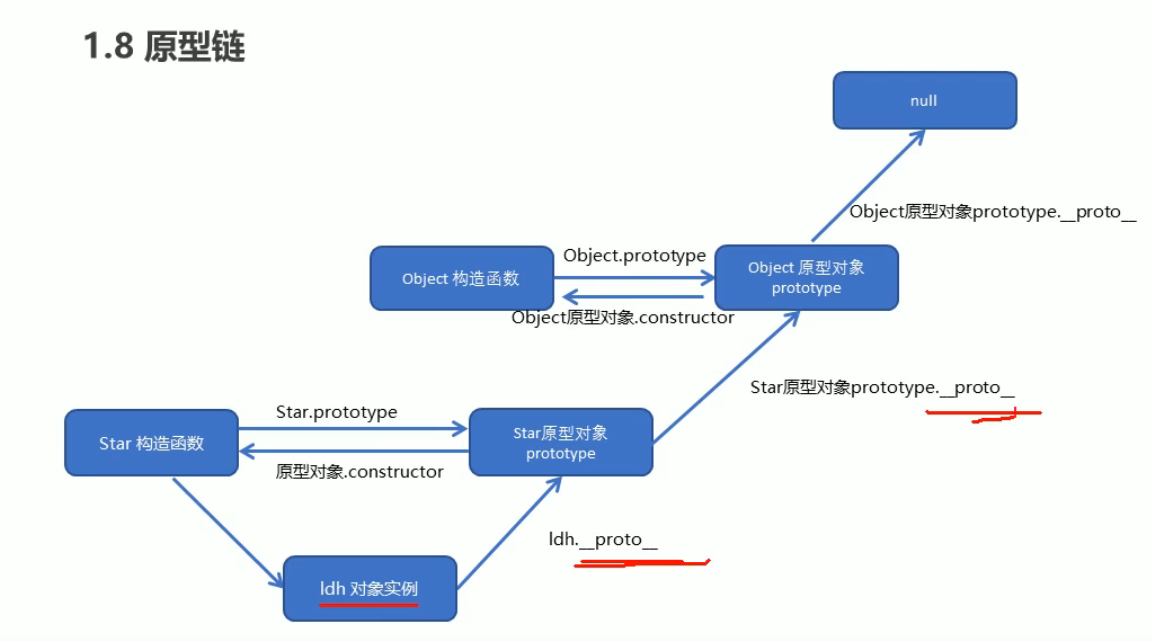
- 当访问一个对象属性时,首先查找这个对象自身
- 如果没有就查找它的原型(也就是
__proto__指向的prototype原型对象) - 如果还没有就查找原型对象的原型(Object的原型对象)
- 一直找到Object为止(null)
__proto__对象原型的意义就是为对象成员查找机制提供一个方向,或者说一条线路。
通过原型对象添加内置对象的方法
javascript
Array.prototype.sum = function() {
var sum = 0;
for (let index = 0; index < this.length; index++) {
sum += this[index];
}
return sum;
}
var arr = [1,2,3]
console.log(arr.sum());
通过构造函数+原型对象实现继承
javascript
// 父构造
function Father(name,age){
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
// 子构造
function Son(name,age,score){
// 调用Father()函数,并将Father中的this指向Son实例对象
Father.call(this,name,age);
this.score = score;
}
// 子类的原型对象指向父类实例,父类实例的__proto__指向父类的原型对象实现继承
Son.prototype = new Father();
// 将原型的构造属性再指回子类的构造方法
Son.prototype.constructor = Son;
var vae = new Son('vae',30,100)